A pre-trained SegResNet model for volumetric (3D) segmentation of the 104 whole body segments
Body CT segmentation models are evolving. Starting from abdominal multi-organ segmentation model [1]. Now the community is developing hundreds of target anatomies. In this bundle, we provide re-trained models for (3D) segmentation of 104 whole-body segments.
This model is trained using the SegResNet [3] network. The model is trained using TotalSegmentator datasets [2].

Figure source from the TotalSegmentator [2].
MONAI Label Showcase
- We highlight the use of this bundle to use and visualize in MONAI Label + 3D Slicer integration.
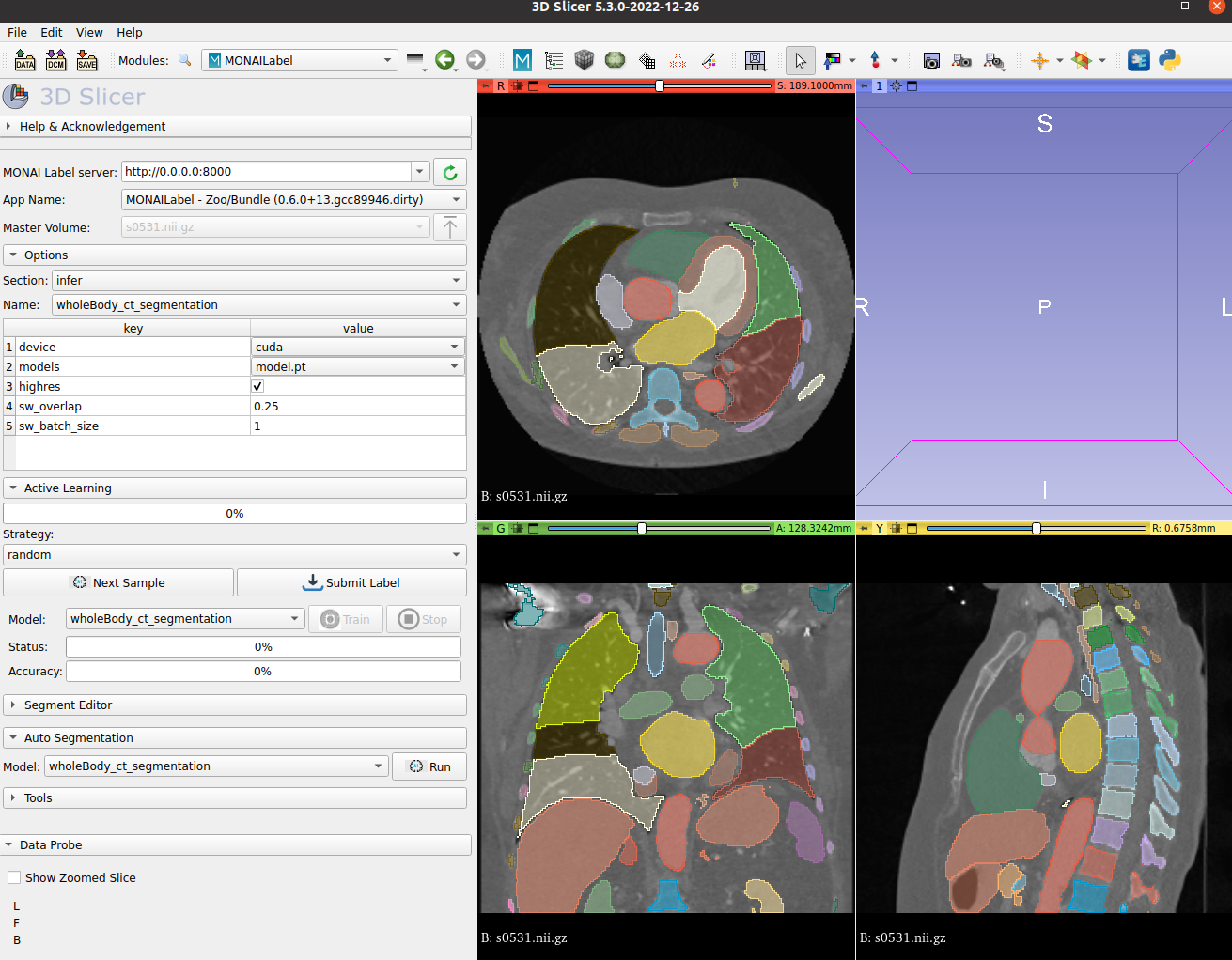
Data
The training set is the 104 whole-body structures from the TotalSegmentator released datasets. Users can find more details on the datasets at https://github.com/wasserth/TotalSegmentator . All rights and licenses are reserved to the original authors.
- Target: 104 structures
- Modality: CT
- Source: TotalSegmentator
- Challenge: Large volumes of structures in CT images
Preprocessing
To use the bundle, users need to download the data and merge all annotated labels into one NIFTI file. Each file contains 0-104 values, each value represents one anatomy class. We provide sample datasets and step-by-step instructions on how to get prepared:
Instruction on how to start with the prepared sample dataset:
- Download the sample set with this link .
- Unzip the dataset into a workspace folder.
- There will be three sub-folders, each with several preprocessed CT volumes:
- imagesTr: 20 samples of training scans and validation scans.
- labelsTr: 20 samples of pre-processed label files.
- imagesTs: 5 samples of sample testing scans.
- Usage: users can add
--dataset_dir <totalSegmentator_mergedLabel_samples>to the bundle run command to specify the data path.
Instruction on how to merge labels with the raw dataset:
- There are 104 binary masks associated with each CT scan, each mask corresponds to anatomy. These pixel-level labels are class-exclusive, users can assign each anatomy a class number then merge to a single NIFTI file as the ground truth label file. The order of anatomies can be found here .
Training Configuration
The segmentation of 104 tissues is formulated as voxel-wise multi-label segmentation. The model is optimized with the gradient descent method minimizing Dice + cross-entropy loss between the predicted mask and ground truth segmentation.
The training was performed with the following:
- GPU: 48 GB of GPU memory
- Actual Model Input: 96 x 96 x 96
- AMP: True
- Optimizer: AdamW
- Learning Rate: 1e-4
- Loss: DiceCELoss
Evaluation Configuration
The model predicts 105 channels output at the same time using softmax and argmax. It requires higher GPU memory when calculating metrics between predicted masked and ground truth. The consumption of hardware requirements, such as GPU memory is dependent on the input CT volume size.
The recommended evaluation configuration and the metrics were acquired with the following hardware:
- GPU: equal to or larger than 48 GB of GPU memory
- Model: high resolution model pre-trained at a slice thickness of 1.5 mm.
Note: there are two pre-trained models provided. The default is the high resolution model, evaluation pipeline at slice thickness of 1.5mm , users can use the lower resolution model if out of memory (OOM) occurs, which the model is pre-trained with CT scans at a slice thickness of 3.0mm .
Users can also use the inference pipeline for predicted masks, we provide detailed GPU memory consumption in the following sections.
Memory Consumption
- Dataset Manager: CacheDataset
- Data Size: 1000 3D Volumes
- Cache Rate: 0.4
- Single GPU - System RAM Usage: 83G
- Multi GPU (8 GPUs) - System RAM Usage: 666G
Memory Consumption Warning
If you face memory issues with CacheDataset, you can either switch to a regular Dataset class or lower the caching rate cache_rate in the configurations within range [0, 1] to minimize the System RAM requirements.
Input
One channel - CT image
Output
105 channels - Label 0: Background (everything else) - label 1-105: Foreground classes (104)
Resource Requirements and Latency Benchmarks
GPU Consumption Warning
The model is trained with 104 classes in single instance, for predicting 104 structures, the GPU consumption can be large.
For inference pipeline, please refer to the following section for benchmarking results. Normally, a CT scans with 300 slices will take about 27G memory, if your CT is larger, please prepare larger GPU memory or use CPU for inference.
High-Resolution and Low-Resolution Models
We retrained two versions of the totalSegmentator models, following the original paper and implementation. To meet multiple demands according to computation resources and performance, we provide a 1.5 mm model and a 3.0 mm model, both models are trained with 104 foreground output channels.
In this bundle, we configured a parameter called highres , users can set it to true when using 1.5 mm model, and set it to false to use the 3.0 mm model. The high-resolution model is named model.pt by default, the low-resolution model is named model_lowres.pt .
In MONAI Label use case, users can set the parameter in 3D Slicer plugin to control which model to infer and train.
- Pretrained Checkpoints
- 1.5 mm model: Download link
- 3.0 mm model: Download link
Latencies and memory performance of using the bundle with MONAI Label:
Tested Image Dimension: (512, 512, 397) , the slice thickness is 1.5mm in this case. After resample to 1.5 isotropic resolution, the dimension is (287, 287, 397)
1.5 mm (highres) model (Single Model with 104 foreground classes)
Benchmarking on GPU: Memory: 28.73G
++ Latencies => Total: 6.0277; Pre: 1.6228; Inferer: 4.1153; Invert: 0.0000; Post: 0.0897; Write: 0.1995
Benchmarking on CPU: Memory: 26G
++ Latencies => Total: 38.3108; Pre: 1.6643; Inferer: 30.3018; Invert: 0.0000; Post: 6.1656; Write: 0.1786
3.0 mm (lowres) model (single model with 104 foreground classes)
GPU: Memory: 5.89G
++ Latencies => Total: 1.9993; Pre: 1.2363; Inferer: 0.5207; Invert: 0.0000; Post: 0.0358; Write: 0.2060
CPU: Memory: 2.3G
++ Latencies => Total: 6.6138; Pre: 1.3192; Inferer: 3.6746; Invert: 0.0000; Post: 1.4431; Write: 0.1760
Performance
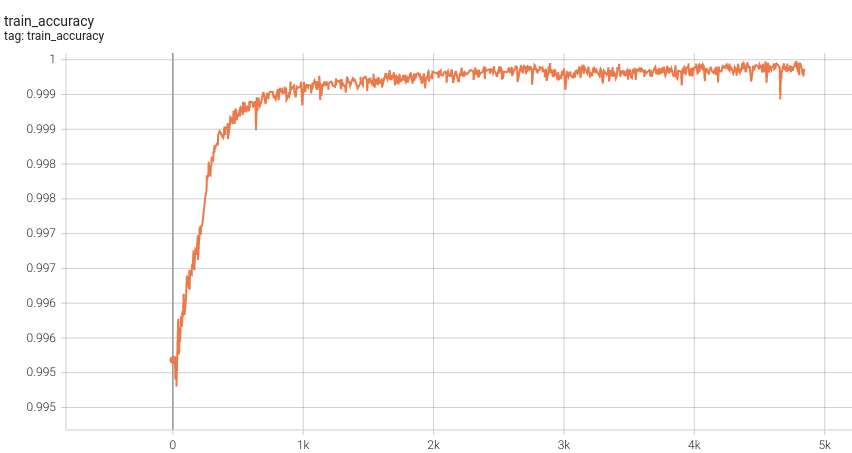
1.5 mm Model Training
Training Accuracy
Validation Dice
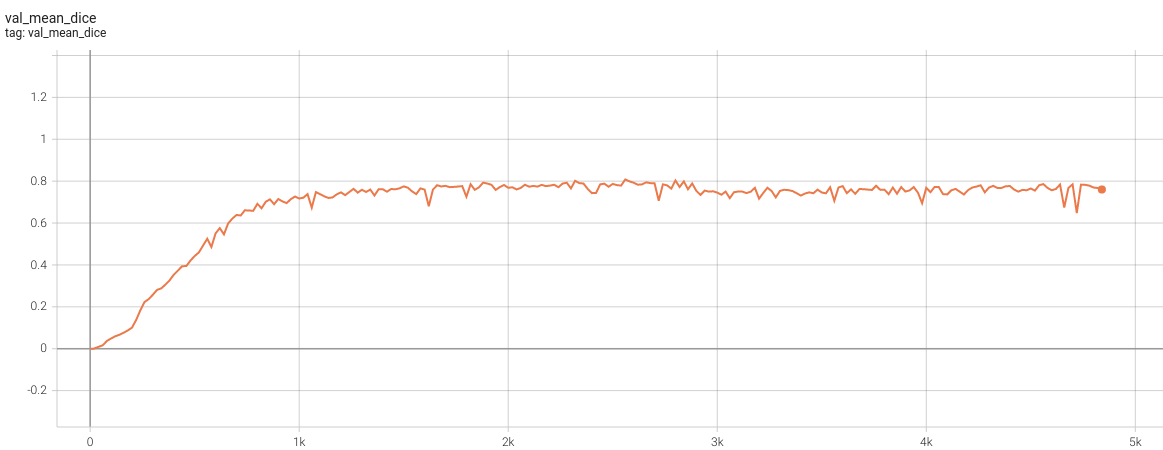
Please note that this bundle is non-deterministic because of the trilinear interpolation used in the network. Therefore, reproducing the training process may not get exactly the same performance. Please refer to https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#reproducibility for more details about reproducibility.
MONAI Bundle Commands
In addition to the Pythonic APIs, a few command line interfaces (CLI) are provided to interact with the bundle. The CLI supports flexible use cases, such as overriding configs at runtime and predefining arguments in a file.
For more details usage instructions, visit the MONAI Bundle Configuration Page .
Execute training:
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file configs/train.json
Please note that if the default dataset path is not modified with the actual path in the bundle config files, you can also override it by using --dataset_dir :
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file configs/train.json --dataset_dir <actual dataset path>
Override the train config to execute multi-GPU training:
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=2 -m monai.bundle run --config_file "['configs/train.json','configs/multi_gpu_train.json']"
Please note that the distributed training-related options depend on the actual running environment; thus, users may need to remove --standalone , modify --nnodes , or do some other necessary changes according to the machine used. For more details, please refer to pytorch’s official tutorial
.
Override the train config to execute evaluation with the trained model:
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file "['configs/train.json','configs/evaluate.json']"
Override the train config and evaluate config to execute multi-GPU evaluation:
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=2 -m monai.bundle run --config_file "['configs/train.json','configs/evaluate.json','configs/multi_gpu_evaluate.json']"
Execute inference:
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file configs/inference.json
Execute inference with Data Samples:
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file configs/inference.json --datalist "['sampledata/imagesTr/s0037.nii.gz','sampledata/imagesTr/s0038.nii.gz']"
References
[1] Tang, Y., Gao, R., Lee, H.H., Han, S., Chen, Y., Gao, D., Nath, V., Bermudez, C., Savona, M.R., Abramson, R.G. and Bao, S., 2021. High-resolution 3D abdominal segmentation with random patch network fusion. Medical image analysis, 69, p.101894.
[2] Wasserthal, J., Meyer, M., Breit, H.C., Cyriac, J., Yang, S. and Segeroth, M., 2022. TotalSegmentator: robust segmentation of 104 anatomical structures in CT images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.05868.
[3] Myronenko, A., Siddiquee, M.M.R., Yang, D., He, Y. and Xu, D., 2022. Automated head and neck tumor segmentation from 3D PET/CT. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.10809.
License
Copyright (c) MONAI Consortium
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the “License”); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an “AS IS” BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
Follow AI Models on Google News
An easy & free way to support AI Models is to follow our google news feed! More followers will help us reach a wider audience!
Google News: AI Models

